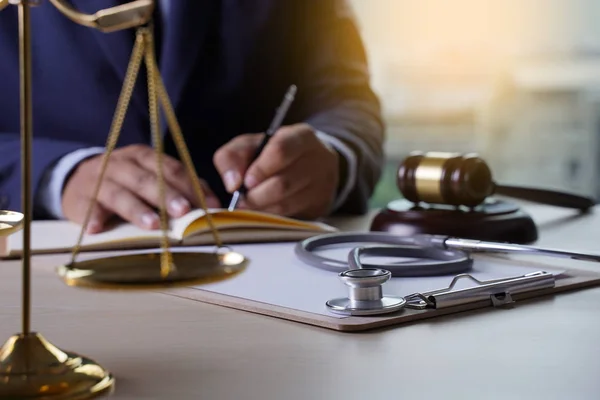
When we entrust our health and well-being to healthcare professionals, we expect them to provide us with the best possible care. Unfortunately, mistakes can happen, and sometimes those mistakes can lead to serious harm.
When this happens, patients have the right to seek compensation for their damages. But what if the harm was not caused by a mistake, but by unethical behavior on the part of the healthcare professional?
This is where the distinction between medical negligence and professional misconduct becomes important. While both can result in harm to patients, they are fundamentally different issues that require different responses.
In this blog post, we will explore the differences between medical negligence and professional misconduct, and why it is important to understand these distinctions.
It doesn’t matter you are a patient seeking justice for harm caused by a healthcare professional, or a healthcare professional seeking to maintain the highest standards of ethics and professionalism, this article will provide you with the information you need to navigate this complex issue.
Medical Negligence
When you seek medical treatment, you expect your healthcare provider to provide appropriate care and treatment. However, sometimes healthcare professionals make mistakes that can lead to harm, injury, or even death. This is known as medical negligence.
Definition
Medical negligence occurs when a healthcare professional fails to provide appropriate care or treatment, or makes a mistake or omission that leads to harm or injury to the patient. It is important to note that medical negligence is not the same as medical malpractice, which involves a breach of duty of care and can result in a lawsuit.
Examples
There are many examples of medical negligence, including:
- Failure to diagnose a condition or disease
- Delayed diagnosis
- Failure to order necessary tests or procedures
- Misdiagnosis
- Surgical errors
- Medication errors
- Failure to obtain informed consent
- Failure to follow standard of care guidelines
- Failure to refer a patient to a specialist.
Proving Medical Negligence
Proving medical negligence can be challenging, but it is necessary to establish negligence in a court of law. To prove medical negligence, you must demonstrate that:
- The healthcare professional had a duty of care to the patient
- The healthcare professional breached that duty of care
- The breach of duty caused harm or injury to the patient
- The harm or injury resulted in damages, such as medical expenses, lost wages, or pain and suffering.
Expert witnesses, medical literature, and scientific evidence can be used to establish the standard of care and whether the healthcare professional breached that standard. In some cases, the legal doctrine of res ipsa loquitor can be used to establish negligence without the need for expert witnesses.
If you believe you have been a victim of medical negligence, it is important to seek the advice of a medical malpractice lawyer. They can help you understand your legal rights and options for seeking compensation for damages.
Overall, it is important to be aware of medical negligence and take steps to protect yourself when seeking medical treatment. This includes asking questions, understanding your treatment options, and being an active participant in your medical care.
Professional Misconduct
When a healthcare professional fails to meet the expected standards of practice in their field, it may amount to professional misconduct. This can result in harm or injury to the patient and may require legal action. In this section, we will discuss the definition, examples, and consequences of professional misconduct.
Definition
Professional misconduct refers to the failure of a healthcare professional to provide care that meets the accepted standards of practice in their field. This can include negligence, lack of ordinary skill, or breach of duty that results in injury or loss to the patient. The plaintiff must usually demonstrate a failure by the professional to perform according to the field’s accepted standards.
Examples
There are many different examples of professional misconduct, such as:
- Failing to meet standards of practice
- Making a mistake during a medical procedure
- Failing to diagnose a medical condition
- Giving incorrect treatment or medication
- Failing to obtain informed consent from the patient
- Failing to follow established protocols or guidelines.
Consequences
The consequences of professional misconduct can be severe and may include:
- Harm or injury to the patient
- Medical expenses and damages
- Loss of income or earning capacity
- Emotional distress and pain and suffering
- Loss of companionship and support.
In cases of professional misconduct, the plaintiff may seek compensation from the healthcare professional or institution responsible for the harm. This can be done through a court of law, and the plaintiff may require the assistance of a medical malpractice lawyer. Expert witnesses may also be called upon to provide testimony regarding the standard of care in the field.
Overall, it is important for healthcare professionals to be aware of the potential consequences of professional misconduct and to take steps to avoid it. This includes following established protocols and guidelines, obtaining informed consent from patients, and staying up-to-date with the latest literature and science in their field.
Differences Between Medical Negligence and Professional Misconduct
Definition
Medical negligence is a term used to describe the failure of a healthcare professional to provide a standard of care that a reasonable person in the same position would have provided, leading to harm or injury to the patient. On the other hand, professional misconduct refers to the behavior of a healthcare professional that falls below the standards of practice and ethics expected of them.
Examples
Medical negligence can occur in various forms, such as failure to diagnose a condition, misdiagnosis, surgical errors, medication errors, and failure to obtain informed consent. Professional misconduct can include inappropriate relationships with patients, breaching patient confidentiality, and failure to maintain proper records.
Legal Implications
Medical negligence can result in a medical malpractice lawsuit where the plaintiff seeks compensation for damages caused by the healthcare professional’s negligence. In contrast, professional misconduct can result in disciplinary action by the relevant licensing board or even criminal charges. The legal implications of professional misconduct can vary depending on the nature of the misconduct and the jurisdiction in which it occurs.
It is essential to note that medical negligence and professional misconduct are not mutually exclusive. A healthcare professional can be guilty of both medical negligence and professional misconduct in the same case. It is also important to remember that not all medical errors or omissions are considered medical negligence or professional misconduct.
To avoid medical negligence and professional misconduct, healthcare professionals must adhere to the duty of care and follow established guidelines and protocols. They must also maintain awareness of any changes in the literature or science related to their field and seek expert witnesses when necessary. In the event of a lawsuit or disciplinary action, healthcare professionals can seek the assistance of malpractice lawyers to defend their case in court.
Preventing Medical Negligence and Professional Misconduct
As a healthcare professional, preventing medical negligence and professional misconduct is crucial to ensure patient safety and avoid legal and ethical implications. Here are some ways to prevent medical negligence and professional misconduct:
Awareness and Education
One of the most effective ways to prevent medical negligence and professional misconduct is to raise awareness and provide education to healthcare professionals. This can be done through training programs, workshops, seminars, and conferences. By educating healthcare professionals about the standard of care, guidelines, and protocols, they can make informed decisions and provide appropriate treatment to patients.
Protocols and Guidelines
Having clear protocols and guidelines in place can also help prevent medical negligence and professional misconduct. These protocols and guidelines should be based on the latest literature and science and should be regularly updated to reflect any changes. They should cover various aspects of medical treatment, including diagnosis, treatment, tests, informed consent, and failure to diagnose.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Healthcare professionals have a legal and ethical duty of care towards their patients. Failing to meet this duty of care can result in medical malpractice, injury, and damages. To prevent medical negligence and professional misconduct, healthcare professionals should be aware of the legal and ethical implications of their actions. This includes understanding their legal responsibilities, following the protocols and guidelines, and seeking expert witnesses when necessary.
To summarise, preventing medical negligence and professional misconduct is essential to ensure patient safety and avoid legal and ethical implications. By raising awareness, providing education, having clear protocols and guidelines, and understanding the legal and ethical implications of their actions, healthcare professionals can provide high-quality medical treatment and avoid medical errors and omissions.
Conclusion
Medical negligence occurs when a healthcare professional unintentionally causes harm to a patient, while professional misconduct refers to unethical behavior by a healthcare professional that puts patients at risk. Patients have the right to seek compensation for damages caused by medical negligence, while professional misconduct should be reported immediately.
YOU SHOULD ALSO READ:
- Medical Malpractice vs Professional Indemnity Insurance: The Key Differences
- Medical Malpractice vs Malfeasance: What are the Key Differences?
- What is Medical Negligence in Health Law? A Clear Explanation
- How Long Can You Go Back to Claim Medical Negligence?
- Medical Law vs Ethics: Understanding the Key Differences